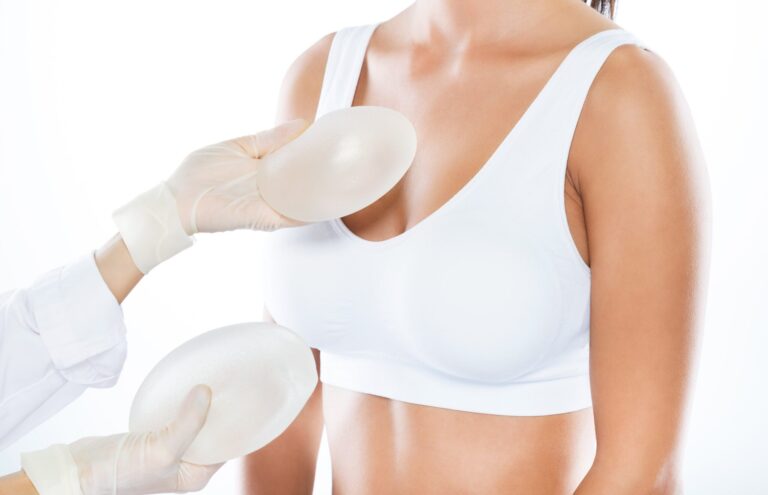
Women always believe that they would look better if they had bigger breasts. Some women are lucky enough to be born with full breasts while some have to spend lots of money and undergo surgery just to get that same effect.
Even though it’s no longer nature-given, a fuller breast with a saline or silicone implant still looks and feels very natural.
There are three incision methods used for breast augmentation using solutions such as saline and silicone and the choice to which of these methods would you want done must be the first thing you need to decide on. Operations on the breast would leave scars but with these incision methods, you can choose the scar placement that would be most convenient to you. The three incision methods being used are; through the nipple, under your arms, and under the breast.
The through the nipple method means that the incision would be around the areola. This is preferred by some because the scars can be easily hidden as there are 2 skin tones in that area. During the operation, the incision is stretched to allow the implants to get inside.
The under the arms incision method is used to keep the scars away from the breasts themselves. The incision is placed under the arms, on the armpit, so they can be concealed easily. The implant is inserted through the openings and it reaches the breasts and under a close look at your breasts, no one would think you actually had implants because the scars are hidden under the arms instead.
Under the breast, incision is most common. The implants are inserted under the breast. The scars there are not very visible as it is hidden.
A simpler method and less invasive is the Macrolane injection. It requires local anaesthetic and it won’t keep the patient away from her daily activities. The Macrolane shot can be regarded as a quick fix before a special event – the patient has an injection performed by a surgeon and the lovely green dress will look better and the bust will be fuller.


